Blockchain software company ConsenSys has recently revised its Privacy Policy and, as a result, outraged many of its users. How does this policy change affect millions of MetaMask users? It’s simple: Metamask logs IPs for every transaction. Many view this as a distinct violation of privacy. What can you do? Read on and find out!
What’s going on?
ConsenSys is the company behind the popular web3 wallet, MetaMask. In the revised Privacy Policy, it was revealed that MetaMask would begin collecting users’ IP addresses and Ethereum wallet addresses during on-chain transactions. This applies to any user that utilizes the default Remote Procedure Call (RPC) provider in MetaMask, Infura, another product of ConsenSys.
Why should I care?
According to ConsenSys, information gathered in this manner may be disclosed to affiliates, during business deals, or to comply with Know Your Customer and Anti-Money Laundering requirements dictated by law enforcement. This is a dire thought for many of the 21M monthly active users of the popular browser wallet.
Infura is currently looking into technical updates to “minimize the collection of personal information, including anonymization techniques and minimization and elimination of any data collection and retention.” But this has left many MetaMask users concerned with their privacy and wondering what can be done.
Especially since the collapse of FTX and the doxing of hundreds of thousands of Celsius users, responsible crypto citizens are seeking safe and secure self-custody options while maintaining the safety of anonymity.
What can I do?
Change your MetaMask RPC
Before we get started on the steps you need to take, I would like to let you know it is practically impossible to use Metamask without it logging your IP. Once you create a new wallet on MetaMask, it will default to Infura as your RPC and send an eth_call to a “BalanceChecker’ contract.
This does not mean that you should do nothing but rather something to be aware of as you take your security measures into your own hands.
Chase Wright has gone through the trouble of switching RPCs on MetaMask and let me tell you, it’s not easy. Note: This guide should work for new and current MetaMask users on Ethereum. The process will be the same for changing RPC providers for other chains.
Step 1: Click on your Wallet icon on the top right and select ‘Settings’

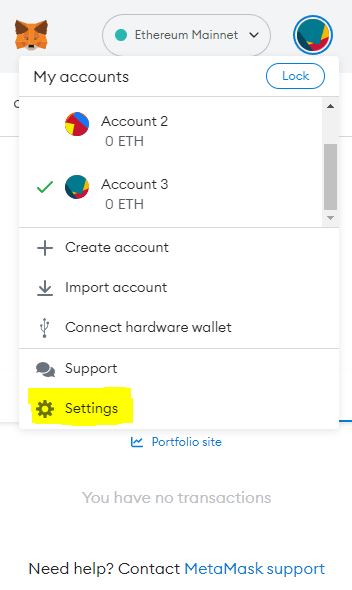
Step 2: Click ‘Networks’ and click ‘Add Network.’ This will open up a separate page on your browser.

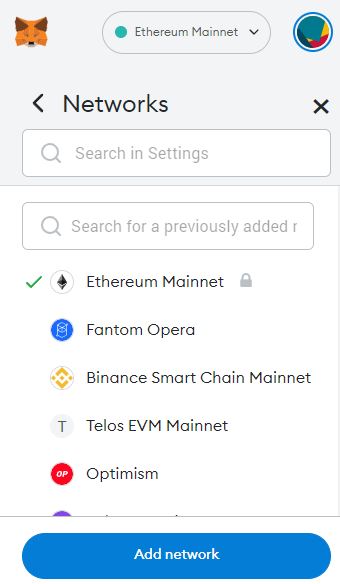
Step 3: On the ‘Add a network’ page, click ‘Add a network manually’
Step 4: You can find a list of RPCs on Chainlist.org. The site provides you with a list of server addresses and scores them based on performance and privacy settings. We would recommend 1RPC as they are heavily committed to defending privacy within the ecosystem but as always, DO YOUR OWN RESEARCH.
Step 5: Once you’ve chosen your RPC, copy the paste the RPC URL into the appropriate field on MetaMask.
The fields should read as follows
Network Name: Ethereum Mainnet
New RPC URL: https://1rpc.io/eth
Chain ID: 1
Currency Symbol: ETH
Block Explorer URL: https://etherscan.io
Step 6: Click Save and your MetaMask wallet will automatically connect to the network through your new RPC.
Switch Wallets
If all this seems too complicated, I would encourage readers to explore different web3 wallets. The wallet market is thriving, with many excellent choices available to users. The Duke of Cryptominister has an excellent thread going over MetaMask alternatives and covers which ones have the appropriate security and privacy measures needed for the discerning crypto user.
A few notes on wallet selection and privacy in general:
- Find a wallet that is open source. Publicly verifiable code will generally have gone through more stress testing than private code.
- Explore their security options. Do they have 2FA? Are you able to add custom RPCs? Do they have appropriate measures in place to protect against IP tracking?
- Consider a VPN provider as an extra layer of security.
Closing Thoughts
Privacy and security should always be at the forefront of a savvy user’s mind. It’s important to constantly assess what information could be out there and what steps you need to take to protect yourself. Self-custody is a right, but it is also a responsibility.














